.NET Technology และ .NET Framework คือ รูปแบบการพัฒนาโปรแกรมแบบใหม่ ที่ไมโครซอพท์ได้พัฒนาออกมาแล้วระยะหนึ่ง โดยมีจุดประสงค์สำคัญคือสามารถใช้งานในสภาวะของฮาร์ดแวร์หรือระบบปฏิบัติการ ที่แตกต่างกันได้อย่างไม่มีปัญหา (เช่น เครื่องพีซีกับเครื่องแมคหรือระบบปฏิบัติการวินโดว์กับลีนุกซ์) และสามารถพัฒนาโปรแกรมใหม่ๆ ได้ด้วยภาษาอะไรก็ได้ให้สามารถทำงานร่วมกันได้ (เช่น ภาษา C กับ Java เป็นต้น) รวมถึงเป็นเครื่องมือในการพัฒนาโปรแกรมให้สามารถเชื่อมต่อกับโปรแกรมต่างๆ ของไมโครซอพท์ได้โดยง่าย ซึ่งก็รวมไปถึงการทำงานภายในของระบบปฏิบัติการวินโดว์เองด้วย ผู้พัฒนาจึงสามารถพัฒนาโปรแกรมใหม่ๆ ได้โดยง่าย และรวดเร็ว ไม่ติดข้อจำกัดต่างๆ อย่างเช่นการพัฒนาโปรแกรมในสมัยก่อนอีกต่อไป
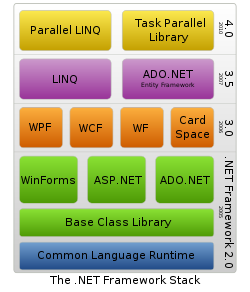
.NET Framework เป็นแพลตฟอร์มสำหรับพัฒนาซอฟต์แวร์ที่รองรับภาษาดอตเน็ตมากกว่า 40 ภาษา ซึ่งมี Library เป็นจำนวนมากสำหรับการเขียนโปรแกรม รวมถึงบริหารการดำเนินการของโปรแกรมบน .NET Framework โดย Library นั้นได้รวมถึงส่วนต่อประสานกับผู้ใช้ การเชื่อมต่อฐานข้อมูล วิทยาการเข้ารหัสลับ อัลกอริทึม การเชื่อมต่อเครือข่ายคอมพิวเตอร์ และการพัฒนาเว็บแอปพลิเคชัน โดย .NET Framework มีส่วนประกอบ ภายในแบ่งออกเป็น 3 ชั้นใหญ่ๆ คือ
1. Programming Language : เป็นรูปแบบของ ภาษา ที่ ออกแบบ มาเพื่อให้สามารถทำงานในสภาวะที่เป็น .NET ได้โดยที่ทาง Microsoft ได้เปิดตัว ภาษาหลัก ๆที่จะใช้ใน การพัฒนา บน .NET นี้ 3ภาษา
C# เป็น ภาษา ใหม่ที่ Microsoft พัฒนา มาจาก C++ กับ JAVA เป็นหลัก
VB.NET เป็น ภาษา ที่ พัฒนา มาจาก Visual Basic ในเวอร์ชั่น 6.0
JScript.net เป็น ภาษา ที่ พัฒนา มาจาก JScript ซึ่งเป็น JavaScript ใน เวอร์ชั่น ของ Microsoft
2. Base Classes Library : Library นั้นเปรียบเสมือน ชุดคำสั่งสำเร็จรูป ย่อยๆที่เพิ่มเข้ามา ซึ่งส่วนใหญ่จะเป็น ชุดคำสั่ง ที่ต้องใช้งานอยู่เป็นประจำ ดังนั้นจึงมีผู้คิดค้น เครื่องอำนวยความสะดวก ใน การเขียนโปรแกรม ซึ่ง Library ใน ภาษา ต่างๆส่วนใหญ่จะอยู่ใน รูปแบบไฟล์ incould แต่ถ้าเป็น ASP สิ่งที่เป็น library ก็คือ component ต่างๆนั่นเอง ซึ่งภายในระบบ .NET จะสร้างสิ่งที่เรียกว่าเป็น Library พื้นฐานขึ้น ทำให้ไม่ว่าจะใช้ ภาษา ใดในการพัฒนา โปรแกรม ก็สามารถที่จะเรียกใช้ Library ที่เป็นตัวเดียวกันได้หมด
3. Common Language Runtime (CLR) : นับเป็น สิ่งสำคัญ แทบจะที่สุดของระบบ .NET นี้ก็ว่าได้ เพราะ CLR ที่ว่านี้มีหน้าที่ทำให้ โปรแกรม ที่เขียนขึ้นมาด้วย ภาษา ต่างๆกัน กลายเป็น ภาษา รูปแบบ มาตรฐาน เดียวกัน ทั้งหมด เราเรียก ภาษา ที่ว่านี้ว่า Intermediate language (IL) ซึ่งเมื่อต้องการที่จะรัน โปรแกรม ใด CLR ที่ว่านี้จะ ตรวจสอบ เครื่องที่รันว่ามี สภาวะแวดล้อม การทำงาน เช่นใดหลังจากนั้นก็จะ คอมไพล์ เป็น โปรแกรม ที่เหมาะสมต่อ การทำงาน ของเครื่องนั้น ทำให้เราสามารถใช้งาน โปรแกรม ต่างๆได้อย่างมี ประสิทธฺภาพสูงสุด ในแต่ละเครื่อง
ผลกระทบเมื่อเลือกใช้งาน .NET Framework Technology
.NET Framework ไม่ใช่เป็น Component ที่ติดตั้งให้ทันทีเมื่อลงระบบปฏิบัติการวินโดว์ XP หรือวินโดว์ 2000 แต่เป็น Component หนึ่งที่สามารถติดตั้งเพิ่มจากแผ่นติดตั้งหรือ Download เพื่อติดตั้งเองได้ ทั้งนี้การติดตั้งนี้ไม่มีค่าใช้จ่ายเรื่องลิขสิทธิ์หรือมีผลกระทบต่อ โปรแกรมที่ได้ติดตั้งอยู่แต่เดิมแต่อย่างไร
โปรแกรมที่พัฒนา .NET Application จะพัฒนาโปรแกรมที่จะได้ภาษากลางที่เรียกว่า Intermediate Language (IL) ที่จะต้องส่งให้ .NET Platform เป็นตัวกลางในการแปลภาษาที่ได้พัฒนาเป็นภาษาเครื่อง (Machine code) อีกทีหนึ่ง ซึ่งแตกต่างจากโปรแกรมที่ไม่ได้พัฒนาด้วย .NET Technology ที่จะพัฒนาแล้วได้ภาษาเครื่องออกมาทันที ซึ่งมีการประมาณว่า ประสิทธิภาพของโปรแกรมที่ทำงานบน .Net Framework นั้น จะได้ประมาณ 80% ของโปรแกรมที่ไม่ได้พัฒนาด้วย .NET Technology (เช่น delphi หรือ Visual Basic 6.0) ทั้งนี้ความแตกต่างจะเห็นได้ชัดขนาดไหนนั้น จะขึ้นกับทรัพยากรของเครื่องด้วย
โปรแกรมที่พัฒนา .NET Application จะถูกควบคุมให้อยู่ในสภาพแวดล้อมที่ควบคุมไว้บน .NET Framework ซึ่งเป็นข้อดีในแง่ของความน่าเชื่อถือของระบบ และผลกระทบที่อาจเกิดขึ้นว่าจะไม่กระทบต่อการทำงานส่วนอื่นๆ โปรแกรมที่พัฒนาด้วย .NET Technology นั้น โดยส่วนใหญ่แล้วจะไม่สามารถเชื่อมต่อโดยตรงให้เข้ากับโปรแกรมที่ไม่ได้พัฒนา ด้วย .NET Technology ได้ การใช้งานร่วมกันระหว่างโปรแกรมจึงเกิดขึ้นเฉพาะระหว่างโปรแกรมที่พัฒนาด้วย .NET Technology อย่างไรก็ดี ทางไมโครซอพต์ได้ออกแบบให้มีทางออกในการเชื่อมต่อกับโปรแกรมอื่นๆ ได้โดยง่ายผ่านเทคโนโลยี Web Service ซึ่งทำให้รูปแบบการทำงานระหว่างโปรแกรมอยู่ในรูปแบบที่เป็นมาตรฐานและเปิด กว้างมากขึ้น
ประโยชน์ที่ได้เมื่อเลือกใช้โปรแกรมที่พัฒนาบน .NET Technology
.NET Framework มีดีและประโยชน์ตรงไหนนั้นพอจะสรุปออกมาได้เป็นข้อๆดังนี้
1. เป็นระบบที่มี Library ที่เป็น มาตรฐาน เดียวกัน เนื่องจากมี Library ที่เป็น มาตรฐานเดียวกัน ทั้งหมดทำให้เราไม่ต้องกังวลว่า ภาษา ที่ใช้เขียนนั้นมี Library ตัวนั้นตัวนี้หรือไม่ รวมทั้งไม่ต้องคอยกังวลว่าถ้าใช้ Library ของ ภาษา หนึ่งแล้วอีก ภาษา หนึ่งจะไม่มี Library ตัวนั้น
2. ไม่ขึ้นกับ ระบบประฏิบัติการ (OS) เนื่องจาก ระบบประฏิบัติการ ที่แต่ละ บุคคล หรือ องค์กร ใช้นั้นย่อมไม่เหมือนกัน แต่ภายใน .NET Framework จะไม่มี ปัญหา นี้ของเพียงแค่มีระบบ .NET Framework ก็จะทำให้สามารถใช้งาน โปรแกรม ต่างๆได้ ซึ่งเป็นข้อดีตรงที่เราจะสามารถใช้โปรแกรมต่างๆได้ทุก ระบบประฏิบัติการ
3. ใช้ในการพัฒนาได้ทุกภาษา ทำให้เราไม่ต้องคอยมา ศึกษา ภาษา ใหม่ ๆ เมื่อต้อง การสร้างโปรแกรม ในแต่ละครั้ง นอกจากนั้น เรายังสามารถเลือก ใช้ ภาษา ที่เราถนัดที่สุดใน การพัฒนาโปรแกรม ต่างๆได้ด้วย
4. มีการควบคุม สิ่งแวดล้อม ในการทำงานเป็นอย่างดี เนื่องจากเป็นระบบที่เป็น มาตรฐาน ทำให้ การควบคุม จัดสรรระบบต่างๆ ทำได้ง่ายขึ้น ไม่ว่าจะเป็นการจัดสรร หน่วยความจำ ด้านการใช้งานเครื่องก็มีความรวดเร็วมากขึ้น ลดโอกาสที่เครื่องจะแฮงค์ได้เป็นอย่างดี
5. ความปลอดภัย ที่มีมากขึ้น .NET Framework สามรถ กำหนดสิทธิ์ การใช้งานหรือ permission ของ ผู้ใช้งาน ได้มากขึ้นทำให้สามารถกำหนดว่า จะให้ โปรแกรม ในส่วนใดใช้งานได้หรือไม่ได้ แล้วแต่เฉพาะบุคคล
เวอร์ชันต่างๆ ของ .NET Framework
Version
Version Number
Release Date
Visual Studio
Default in Windows
1.0
1.0.3705.0
2002-02-13
Visual Studio .NET
1.1
1.1.4322.573
2003-04-24
Visual Studio .NET 2003
Windows Server 2003
2.0
2.0.50727.42
2005-11-07
Visual Studio 2005
Windows Server 2003 R2
3.0
3.0.4506.30
2006-11-06
Windows Vista, Windows Server 2008
3.5
3.5.21022.8
2007-11-19
Visual Studio 2008
Windows 7, Windows Server 2008 R2
4.0
4.0.30319.1
2010-04-12
Visual Studio 2010
4.5
4.5.40805
2011-09-13 (Developer Preview)
Visual Studio 11
Windows 8, Windows Server 8
ฟีเจอร์ต่างๆของแต่ละเวอร์ชัน
.NET Framework 1.1
Built-in support for mobile ASP.NET controls. Previously available as an add-on for .NET Framework, now part of the framework.
Security changes – enable Windows Forms assemblies to execute in a semi-trusted manner from the Internet, and enable Code Access Security in ASP.NET applications.
Built-in support for ODBC and Oracle databases. Previously available as an add-on for .NET Framework 1.0, now part of the framework.
.NET Compact Framework – a version of the .NET Framework for small devices.
Internet Protocol version 6 (IPv6) support.
Numerous API changes.
NET Framework 2.0
The 2.0 Redistributable Package can be downloaded for free from Microsoft, and was published on 22 January 2006.
The 2.0 Software Development Kit (SDK) can be downloaded for free from Microsoft.
It is included as part of Visual Studio 2005 and Microsoft SQL Server 2005.
Version 2.0 without any Service Pack is the last version with support for Windows 98 and Windows Me. Version 2.0 with Service Pack 2 is the last version with official support for Windows 2000 although there have been some unofficial workarounds published online to use a subset of the functionality from Version 3.5 in Windows 2000.] Version 2.0 with Service Pack 2 requires Windows 2000 with SP4 plus KB835732 or KB891861 update, Windows XP with SP2 or later and Windows Installer 3.1 (KB893803-v2)
It shipped with Windows Server 2003 R2 (not installed by default).
Changes in 2.0 in comparison with 1.1
Generics
Language support for generics built directly into the .NET CLR.
Full 64-bit support for both the x64 and the IA-64 hardware platforms.
Numerous API changes.
SQL Server integration – .NET 2.0, VS 2005, and SQL Server 2005 are all tied together. This means that instead of using T-SQL, one can build stored procedures and triggers in any of the .NET-compatible languages.
A new hosting API for native applications wishing to host an instance of the .NET runtime. The new API gives a fine grain control on the behavior of the runtime with regards to multithreading, memory allocation, assembly loading and more (detailed reference). It was initially developed to efficiently host the runtime in Microsoft SQL Server, which implements its own scheduler and memory manager.
Many additional and improved ASP.NET web controls.
New data controls with declarative data binding.
New personalization features for ASP.NET, such as support for themes, skins, master pages and web parts.
.NET Micro Framework – a version of the .NET Framework related to the Smart Personal Objects Technology initiative.
Membership provider
Partial classes
Nullable types
Anonymous methods
Iterators
Data tables
.NET Framework 3.0
.NET Framework 3.0, formerly called WinFX was released on 21 November 2006. It includes a new set of managed code APIs that are an integral part of Windows Vista and Windows Server 2008 operating systems. It is also available for Windows XP SP2 and Windows Server 2003 as a download. There are no major architectural changes included with this release; .NET Framework 3.0 uses the Common Language Runtime of .NET Framework 2.0. Unlike the previous major .NET releases there was no .NET Compact Framework release made as a counterpart of this version. Version 3.0 of the .NET Framework shipped with Windows Vista. It also shipped with Windows Server 2008 as an optional component (disabled by default).
.NET Framework 3.0 consists of four major new components:
Windows Presentation Foundation (WPF), formerly code-named Avalon; a new user interface subsystem and API based on XML and vector graphics, which uses 3D computer graphics hardware and Direct3D technologies. See WPF SDK for developer articles and documentation on WPF.
Windows Communication Foundation (WCF), formerly code-named Indigo; a service-oriented messaging system which allows programs to interoperate locally or remotely similar to web services.
Windows Workflow Foundation (WF) allows for building of task automation and integrated transactions using workflows.
Windows CardSpace, formerly code-named InfoCard; a software component which securely stores a person's digital identities and provides a unified interface for choosing the identity for a particular transaction, such as logging in to a website.
.NET Framework 3.5
Version 3.5 of the .NET Framework was released on 19 November 2007, but it is not included with Windows Server 2008. As with .NET Framework 3.0, version 3.5 uses the CLR of version 2.0. In addition, it installs .NET Framework 2.0 SP1, (installs .NET Framework 2.0 SP2 with 3.5 SP1) and .NET Framework 3.0 SP1 (installs .NET Framework 3.0 SP2 with 3.5 SP1), which adds some methods and properties to the BCL classes in version 2.0 which are required for version 3.5 features such as Language Integrated Query (LINQ). These changes do not affect applications written for version 2.0, however.
As with previous versions, a new .NET Compact Framework 3.5 was released in tandem with this update in order to provide support for additional features on Windows Mobile and Windows Embedded CE devices.
The source code of the Base Class Library in this version has been partially released (for debugging reference only) under the Microsoft Reference Source License.
Service Pack 1
The .NET Framework 3.5 Service Pack 1 was released on 11 August 2008. This release adds new functionality and provides performance improvements under certain conditions,[9] especially with WPF where 20-45% improvements are expected. Two new data service components have been added, the ADO.NET Entity Framework and ADO.NET Data Services. Two new assemblies for web development, System.Web.Abstraction and System.Web.Routing, have been added; these are used in the ASP.NET MVC Framework and, reportedly, will be utilized in the future release of ASP.NET Forms applications. Service Pack 1 is included with SQL Server 2008 and Visual Studio 2008 Service Pack 1. It also featured a new set of controls called "Visual Basic Power Packs" which brought back Visual Basic controls such as "Line" and "Shape". Version 3.5 SP1 of the .NET Framework shipped with Windows 7. It also shipped with Windows Server 2008 R2 as an optional component (disabled by default).
.NET Framework 3.5 SP1 Client Profile
For the .NET Framework 3.5 SP1 there is also a new variant of the .NET Framework, called the ".NET Framework Client Profile", which at 28 MB is significantly smaller than the full framework and only installs components that are the most relevant to desktop applications. However, the Client Profile amounts to this size only if using the online installer on Windows XP SP2 when no other .NET Frameworks are installed. When using the off-line installer or any other OS, the download size is still 250 MB.
.NET Framework 4
Key focuses for this release are:
Parallel Extensions to improve support for parallel computing, which target multi-core or distributed systems. To this end, technologies like PLINQ (Parallel LINQ), a parallel implementation of the LINQ engine, and Task Parallel Library, which exposes parallel constructs via method calls. are included.
New Visual Basic .NET and C# language features, such as implicit line continuations, dynamic dispatch, named parameters, and optional parameters.
Support for Code Contracts.
Inclusion of new types to work with arbitrary-precision arithmetic (System.Numerics.BigInteger) and complex numbers (System.Numerics.Complex).
ข้อมูล: www.netregis.com/asp.html, http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/.NET_Framework_version_history
อ่านต่อที่นี่ http://notebookspec.com/web/?p=88056
ไม่มีความคิดเห็น:
แสดงความคิดเห็น
หมายเหตุ: มีเพียงสมาชิกของบล็อกนี้เท่านั้นที่สามารถแสดงความคิดเห็น